1. Introduction to Technical SEO
Technical SEO is all about making sure search engines can find and understand your website. Unlike the content side of SEO, which focuses on keywords and writing for people, technical SEO is what happens behind the scenes—site speed, mobile usability, security, and how easily search engines can crawl your site.
For businesses in Dubai, technical SEO can make a big difference. With so many businesses competing online, having a fast, secure, and easy-to-navigate site keeps people around longer and helps boost your site’s rank in search engines.
In this guide, we’ll go over the main parts of technical SEO, explain why each one matters, and offer simple steps you can take to improve your site. By the end, you’ll have a solid plan to make your website a little smoother for search engines and more welcoming for your visitors. If you want to learn about on page seo you can read it here. Now Let’s dive in.
2. Core Elements of Technical SEO
To get the basics of technical SEO right, it helps to understand a few core areas that affect how search engines see and rank your site. Let’s go over some of these key parts, starting with crawling and indexing and moving into site structure and navigation.
Site Crawling and Indexing
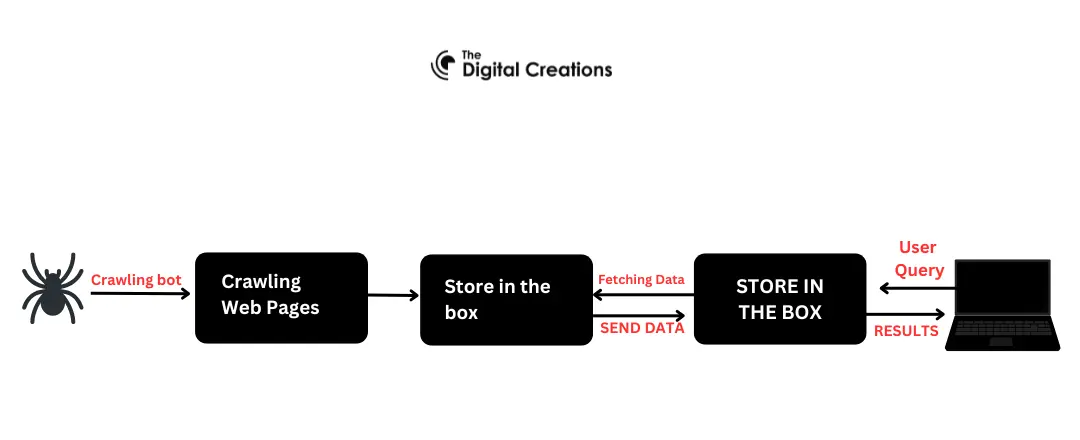
Search engines like Google use bots (often called “crawlersâ€) to explore websites, find pages, and add them to their indexes. If a page isn’t indexed, it won’t appear in search results, no matter how well-written or optimized it is. This makes crawlability and indexing fundamental to any SEO strategy.
Crawl Errors
Crawl errors happen when a bot can’t access certain pages. These errors can come from broken links, server issues, or restricted access settings. By identifying and fixing crawl errors, you ensure that search engines can fully understand what’s on your site.
XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap acts like a roadmap for search engines, guiding them to your website’s main pages. It’s a simple file that lists the URLs you want indexed. Many content management systems, like WordPress, allow you to create sitemaps automatically, but you can also submit one through Google Search Console for extra assurance.
Robots.txt
The robots.txt file tells search engines which pages to crawl and which ones to skip. This can be useful if you have sections of your website (like test pages or duplicated content) that you don’t want indexed. Keep this file clean and updated to avoid blocking important pages by accident.
Website Structure and Navigation
A well-organized site makes it easy for both visitors and search engines to find content. Search engines prefer a logical structure, where related pages are grouped together, usually through a clear menu and proper internal linking.
Internal Linking
Internal links connect one page of your site to another, helping users navigate and encouraging search engines to crawl more of your site. Think of internal links as guides that show both visitors and bots where to go next.
SEO Best Practices for Navigation
For the best results, keep your menu clear and intuitive, with category pages that make sense for your content. This approach also benefits user experience, as people are more likely to stay on a site that’s easy to browse. The less effort it takes to find content, the better.
3. Optimizing Page Load Speed
One of the most crucial aspects of technical SEO is page load speed. Simply put, how fast your website loads affects both user experience and search rankings. Slow load times often lead to higher bounce rates, as visitors quickly leave websites that take too long to load. Fortunately, there are a few simple steps to help you improve speed and keep visitors engaged.
Tools for Measuring Site Speed

A good starting point for understanding your site’s speed is to use tools designed to measure performance. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix can give you a detailed breakdown of your website’s load time, along with specific areas for improvement. These tools also highlight elements such as image size, server response time, and resource usage, making it easier to identify and address slow-loading areas on your site.
Improving Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals is a set of metrics Google uses to measure site performance, and improving these metrics can have a significant impact on your SEO.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This measures how quickly the main content of your page loads. Aim for an LCP of 2.5 seconds or less to provide a good user experience.
First Input Delay (FID): This gauges the time it takes for your website to respond after a user first interacts with it. A low FID, ideally less than 100 milliseconds, helps keep users engaged.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This measures how stable your layout is as it loads, helping you avoid annoying shifts that can lead users to accidentally click the wrong element.
To improve these metrics, consider compressing images, enabling browser caching, and using lazy loading, which delays the loading of off-screen images until the user scrolls down. These adjustments reduce the amount of data your website needs to load, making it faster and more efficient.
4. Mobile-Friendliness
With more people browsing on mobile than ever, mobile-friendliness is essential for both user experience and SEO. Google now uses mobile-first indexing, which means it primarily considers the mobile version of your site when determining rankings. If your site isn’t optimized for mobile, you risk losing out on both search visibility and mobile traffic.
Why Mobile Optimization Matters
A mobile-friendly website adapts smoothly to any screen size, ensuring a seamless experience for visitors, whether they’re on a desktop or smartphone. In Dubai, where mobile usage is high, a mobile-optimized site helps capture a larger audience, keeping users on the page longer and lowering bounce rates.
Steps to Optimize for Mobile
Responsive Design
Implement a responsive design that automatically adjusts to fit the user’s screen size. Most modern website platforms offer responsive design options, but it’s worth testing your site to ensure everything looks and functions well on smaller screens.
Clickable Elements
On mobile devices, make sure that buttons and links are large enough to be easily tapped. This prevents users from accidentally clicking the wrong link and improves overall usability.
Page Load Speed on Mobile
Page load speed is even more critical on mobile, where network speeds can vary. Compress images, reduce redirects, and consider using AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) for faster loading on mobile. AMP strips down unnecessary code, making pages lightweight and quick to load.
Testing with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test Tool
Google offers a Mobile-Friendly Test tool to analyze how well your site performs on mobile devices. This tool provides specific recommendations to help improve your mobile site, ensuring it meets the standards of mobile-first indexing.
5. Securing Your Website
Security is crucial for both search engines and visitors. A secure site not only protects user data but also impacts SEO. Google has made security a ranking factor, favoring sites that prioritize user safety, which makes HTTPS essential for technical SEO.
Why HTTPS Matters
When your website uses HTTPS instead of HTTP, data exchanged between your site and its users is encrypted. This prevents sensitive information—like passwords, credit card numbers, and personal data—from being intercepted. Beyond security, HTTPS is a trust signal to visitors, showing them that your site is safe to use. For businesses in Dubai, where online shopping and services are on the rise, a secure connection builds trust and can boost conversion rates.
Steps to Secure Your Website

Install an SSL Certificate
An SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate is what enables HTTPS. Most hosting providers offer SSL certificates, and some platforms, like Let’s Encrypt, provide free options. Once installed, the SSL certificate will automatically encrypt the data passing through your site.
Enable HTTPS Across All Pages
After getting an SSL certificate, ensure that every page of your website loads with HTTPS. Google Search Console can help identify any remaining non-secure pages that need updating.
Check for Mixed Content
Mixed content occurs when HTTPS pages include links or resources (like images or scripts) served over HTTP. This can create security warnings for visitors and negate the benefits of HTTPS. Regularly scan your site for mixed content and update any insecure links or resources to HTTPS.
Use Security Plugins
If your website is built on a platform like WordPress, consider using a security plugin to protect against common threats like brute-force attacks, malware, and spam. Popular security plugins include Wordfence and Sucuri, which offer various tools to enhance site security.
By following these steps, you’re not only safeguarding your visitors’ data but also aligning with Google’s security preferences, which can help improve your search rankings.
6. Fixing Common Technical SEO Issues
Every website can run into technical SEO issues now and then, but staying on top of these problems is crucial for maintaining search visibility. Addressing common technical problems like broken links, duplicate content, and missing metadata helps ensure that both search engines and users have a smooth experience on your site.
Identifying and Resolving Common Issues
Broken Links
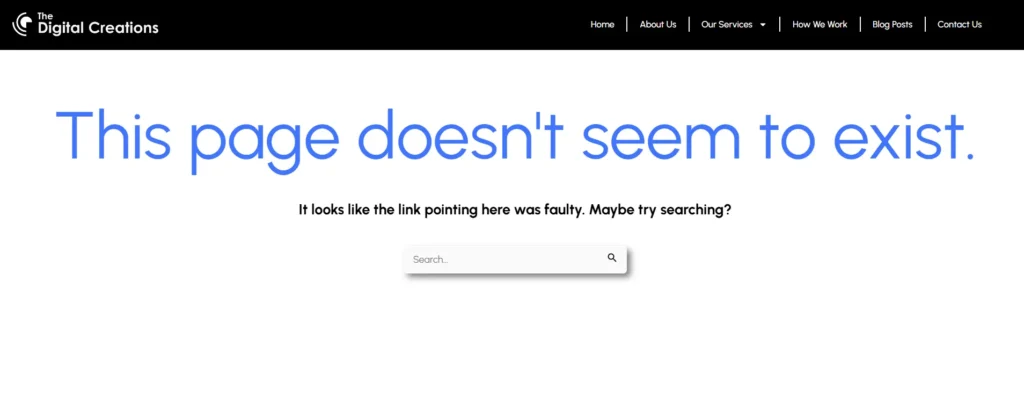
Broken links, or “404 errors,†occur when a page is missing or its URL has changed. These links disrupt user experience and waste crawl budget, which can impact SEO. Use tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console to find broken links, then update them or redirect them to relevant pages.
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content confuses search engines about which version of a page to rank, potentially diluting your SEO efforts. This issue can arise from similar pages, or even variations in URLs. Using canonical tags on duplicate or similar pages signals which version is the main one to index, helping to consolidate SEO value.
Missing or Poorly Optimized Metadata
Metadata like title tags and meta descriptions tell search engines what your page is about. Missing or vague metadata can limit visibility and engagement in search results. Aim for clear, keyword-rich titles (under 60 characters) and descriptions (under 160 characters) that accurately reflect each page’s content.
Structured Data Markup
Adding structured data, or schema markup, enhances search engines’ understanding of your content, which can improve rankings and generate rich snippets in search results. For example, e-commerce sites can use schema to display product information like prices and reviews directly on the search results page.
Monitoring for Issues Regularly
Consistent monitoring helps catch technical SEO issues early. Google Search Console is a free tool that alerts you to many common issues, including crawling errors and mobile usability problems. By setting up regular checks, you can ensure that your site stays optimized and maintains its performance in search results.
FAQs on Technical SEO
1. What is technical SEO, and why does it matter?
Technical SEO involves optimizing the backend of a website to help search engines crawl, index, and understand the content more effectively. It matters because a well-optimized website enhances user experience, improves rankings on search engines, and helps attract more organic traffic.
2. How can I check if my website is optimized for SEO?
You can use tools like Google Search Console for a detailed look at your site’s technical health. Other tools, such as Screaming Frog and SEMrush, also provide insights into issues like broken links, duplicate content, and page load speeds that can impact SEO.
3. What is a sitemap, and how does it impact SEO?
A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on your website, helping search engines understand its structure and prioritize important content. Submitting a sitemap to Google via Search Console can speed up the indexing of your pages and improve your SEO performance.
4. How can I make my website load faster?
To improve load speed, consider compressing images, using browser caching, and minimizing large files like JavaScript and CSS. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights can offer specific suggestions for boosting your website’s speed.
5. Is there any difference between HTTP and HTTPS?
HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP, which encrypts data between a website and its users. Google prioritizes HTTPS sites for security, making it a necessary component of technical SEO for improved rankings and user trust.
6. Does technical SEO involve content creation?
While technical SEO doesn’t directly involve writing content, it does support content by ensuring that search engines can access and understand it. By improving website structure and speed, technical SEO indirectly enhances the impact of your content.
7. How often should I conduct a technical SEO audit?
Performing a technical SEO audit every 3–6 months is recommended, especially for websites with frequent updates. Regular audits help catch issues early and keep your site optimized for search engines.
